Vet's Corner
- Vet's Corner
- Disease Syndromes
- Abortion in Angora goats
- Anaemia
- Birth abnormalities in Angora kids
- BLINDNESS or ‘Apparent Blindness’ in Angora Goats
- Diarrhoea in Angora Goats
- Tulp - Morea spp
- EYE - BLUE DISCOLOURATION
- Floppy Kid Syndrome
- Hair loss in Angora Goats
- Icterus, Jaundice, 'Geelsig'
- Itching (Pruritic) Angora goats
- Lameness in Angora Goats
- Neurological Signs
- PHOTOSENSITIVITY in Angora goats
- Red Urine in Angora Goats
- Sudden death in Angora Goats
- 'Swelsiekte' - Swelling disease in Angora Goats
- SWELLING DISEASE (Swelsiekte) - Is this the answer?
- Swollen Joints
- SWOLLEN HEAD ‘DIKKOP’ IN ANGORA GOATS
- Diseases
- Abortion - Brucellosis melitensis
- Abortion - Enzootic abortion
- Abscess in Angora Goats
- ACIDOSIS
- Abscess – Foot Abscess ‘Sweerklou’
- Abscess - Trueperella pyogenes
- Abscess - Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
- Anthrax (Miltsiekte)
- Bladder Stones
- Bloat in Angora Goats
- Bluetongue in Angora Goats?
- Botryomycosis – Pyogranulomatous bacterial infection in Angora goats
- Campylobacter
- Cancer- Heart (Sarcoma)
- Cancer - Jaw
- Cancer - Skin
- CCPP (Contagious Caprine Pleuropneumonia)
- Cerebral Gliosis and Spongiosis in Angora goats
- Clostridium Chauvoei - 'Sponsiekte’ Blackquarter
- Clostridiun Haemolyticum - Bacilliary Haemogloninuria ‘Red Water’
- Clostridium Novyi Type A - Dikkop Swelled Head
- Clostridium Novyi Type B – infectious necrotic hepatitis, black disease
- Clostridium perfringens Toxins
- Clostridium Perfringens Type A
- Clostridium Perfringens Type B
- Clostridium Perfringens Type C - Necrotic Enteritis
- Clostrdium Perfingens Type D
- Clostridium septicum - 'baarmoedersponssiekte'
- Cold (Hypothermia) and the Angora goat
- Cold - Why Angora Goats are More Susceptible in Summer than Winter
- Cretinism (Iodine Deficiency) In Angora Goat Kids
- Cryptosporidiosis in Angora Goats
- Diarrhoea in Angora Goats
- Domsiekte
- Draaisiekte
- Eperythrozoonosis (Mycoplasma ovis)
- Escherichia coli (E.coli)
- Fly Strike, Myiasis, ‘Brommers’
- Foot and Mouth Disease
- Footrot 'Vrotpootjie'
- 'Gallsickness' Anaplasmosis
- Graaff-Reinet disease - Maedi-Visna
- Hair loss in Angora Goats- Dermatophilosis
- Hair Loss in Angora Goats - Hypersensitivity Dermatitis
- Hair Obstruction (Trichobezoar) in an Angora goat kid
- Hairy Shaker Disease (Border disease)
- Heartwater
- Hypocortisolism in Angora Goats
- Johne's Disease
- Joint –ill (Angora Kids)
- Kid Mortality
- Leptospirosis
- Listeriosis
- Lymphocytic-Plasmacytic Enteris (LPE) IN ANGORA GOATS
- Mastitis 'Blue Udder' 'blou-uier'
- Meningoencephalitis (bacterial) in Angora goat kids
- Milk Fever, Parturient paresis
- 'Opthalmia' 'pink eye' 'aansteeklike blindheid'
- Polioencephalomalacia. Vit B1 deficiency
- Orf in Angora Goats
- Papillomavirus and Fibropapillomas in Angora goats
- Paralysis tick
- Pneumonia
- Peestersiekte
- Peste des petits (PPR)
- Phytobezoariasis (Plant hair balls)
- Pseudomonas infection in Angora goats
- Prolapse of Vagina, Rectum or Uterus
- Q-fever, Coxiella
- Rabies
- Rift Valley Disease
- Rhodococcus equi infection in Angora goats
- Salmonella
- Spring Lamb Paralysis
- Testicle Abnormalities in Angora Goats
- Tetanus
- Toxoplasmosis
- 'Twisted gut' 'Draaiderm' 'Rooiderm'
- Wesselsbron Disease
- Drugs
- Anthelmintic Drug Classification
- Anthelmintic Drug Lists update (Ontwurmmiddels)
- Anthelmintic Resistance
- Closantel Toxicity
- Coccidiosis- Baycox and Vecoxan in weaned Angora kids
- Coccidiosis- off label treatments
- Combination Doses Better
- Dipping Guidelines - Ectoparasite Treatment
- Dipping Guidelines - Washing of Angora Goats
- Drugs for treating Coccidiosis in Angora Kids
- Ectoparasites Drug List
- EKO water trough tablets
- Fipronil, Abamectin (Atilla)
- Ivermectin Toxicity
- Levamizole Toxicity
- Lice Treatment
- Pain Relief Guidance
- Pain Relief Guidance- Off label drugs
- Pour-on Products Application to Alternative Sites
- Field Studies
- Aloe Ferox
- Albumin: A predictor of survival rates in Angora goat kids
- Breeding worm resistant Angora's
- Coccidiosis- Baycox and Vecoxan in weaned Angora kids
- Coccidiosis- off label treatments
- Crypto - Screening for sub-clinical carriers
- Faecal egg and tick counts following treatment with Aloe Ferox
- Foot Abscess 'Sweerklou' Trial
- Lice Off-Label Treatment
- Lymphocytic-Plasmacytic Enteritis (LPE) in Angora Goats: Treatment - Field_Study
- Off-Label Coccidiosis Treatments- Angora goat kids
- Rift Valley Fever Seroconversion
- Rift Valley Fever (RVF) - Vaccinating maiden ewes each year
- Swelling Disease (Swelsiekte)
- Testicle Traits
- The Composition of Interstitial Fluid in Angora Goats
- The effect of Brevibacillus laterosporus (bioworx NEMAPRO) on internal parasites in Angora goats
- The impact of Brown Stomach worm (and Coccidiosis) on Angora Kids
- Treatment following Brown Stomach Worm and Cocidiosis infection
- Treatment of Lice, Ticks and Roundworms in Angora Goats
- Nutrition
- Amino Acid Requirements for Mohair Fibre
- BST use in Angora Goats
- Cobalt, Vit B12
- Copper Deficiency
- Copper Toxicity 'Geelsiekte'
- Drought Feeding
- Effect of Season on Mohair Fibre Diameter
- Effect on Mohair quality traits
- Feeding Ewes in Good Seasons - Is it Economical?
- Feeding Hansies
- Feeding weaned Angora kids
- Flush Feeding
- Goitre and Hypothyroidism (Iodine deficiency) in Angora goats
- Growth Rate of Angora Kids
- Hair Loss in Angora Goats - Nutritional Causes
- Importance of METHIONINE in Angora goats
- Licks Lekke
- Lucerne
- Maize/Mealies - Feed whole or finely ground?
- Maximising Production
- Milk production by the Angora Ewe
- Mineral analysis of the liver of goats
- Mineral and Vitamin Options
- PHOSPHORUS (P) Deficiency
- Polioencephalomalacia. Vit B1 deficiency
- Pregnant and Lactating Ewe
- Protein: How much of a good thing?
- PROTEIN what do the terms mean?
- Salt in Angora Goats
- Selenium Deficiency- White Muscle Disease
- Selenium Supplementation
- The Effect on Mohair Production
- The importance of Fibre when feeding Angora goats
- Urea Poisoning
- VITAMIN AND MINERAL SUPPLEMENTS REQUIREMENTS FOR ANGORA GOATS
- Weaning and the First 18 Months
- Whats in a bag of feeds?
- When should we feed Angora ewes?
- When to Give Supplementary Feed
- White Muscle Disease in Angora Goats
- ZINC Deficiency
- Parasites
- Angora Goats have Paler Mucous Membranes
- Brandsiekte
- Breeding worm resistant Angora's
- Brown Stomach Worm
- Coccidiosis
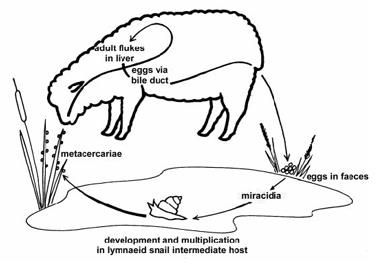
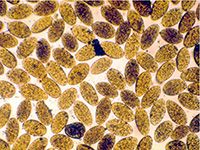
- Conical Fluke
- Diatomaceous Earth as an alternative treatment for internal parasites
- EKO water trough tablets
- Faecal Egg Count (FEC)
- Hair Loss in Angora Goats - External Parasites
- Immunity in Angora goats
- Lungworm in Angora goats
- Lice and Angora Goats
- Liver Fluke in Angora Goats
- Nasal Worm
- Roundworm Management Strategies
- Targeted Selective Treatment (TST)
- Tape Worm
- The impact of Brown Stomach worm (and Coccidiosis) on Angora Kids
- Ticks
- Warble Fly
- Wireworm/Haarwurm
- 'Uitpeuloog' Gedoelstia
- Poisoning
- Asbos - Mesembryantheium
- Aflatoxicosis
- American Aloe (Agave americana) 'Garingboom'
- Asaemia axillaris – ‘Vuursiektebossie’
- Botulism 'Lamsiekte'
- Closantel Toxicity
- Copper Toxicity 'Geelsiekte'
- Cynanchum spp (bobbejaantou)
- Datura (Stinkblaar) poisoning in Angora Kids
- Dikoor: Panicum spp- Buffalo grass
- Diplodia maydis (Diplodiosis) - Harvested maize
- 'Geeldikkop' Tribulus terrestris
- GANSKWEEK
- Lonophore Poisoning
- Ivermectin Toxicity
- 'Kaalsiekte' 'Lakteersiekte'
- 'Kisieblaar' Malva Parviflora
- Mesembryanthemum and Opuntia Spp (Vygies and Turksvry)
- Mexican Poppy- Argemone Mexicana
- Nitrate Poisoning
- Krimpsiekte (Cardiac Glycosides)
- ‘Kweek Tremors’, Cynodum dactylon
- Levamizole Toxicity
- Melia azedarach (Syringa berry)
- 'MELKBOS' Euphorbia mauritanica
- 'MELKTOU' Sarcostemma viminale
- mycotoxins
- Nenta, Plakkies, Pigs ears - Kalanchoe, Cotyledon spp
- Organophosphate containing dip
- Pithomyces chartarum- ‘Stellenbosch photosensitivity
- Prussic acid Poisoning 'Geilsiekte'
- Pteronia pallens- witbossie, Scholtz-bossie
- Salt Poisoning
- SATANSBOS, Silver-leaf nightshade.
- Slangkop - Drimia spp
- ‘Springbokbossie’ ‘Malkopharpuis’ Hertia pallens
- Tulp - Morea spp
- Urea Poisoning
- Vermeersiekte
- Waterpens
- 'WITSTORM' 'VAALSTORM' Thesium spp.
- Reproduction
- Artificial Insemination
- Breeding a Hardy Angora Goat
- Dystocia - Difficult Births
- Ewe AgeEffect on Reproduction
- Ewe Selection
- GENOMICS- Genetic selection potential (parasites, disease and production parameters)
- Impact of Shearing on Reproduction
- Kid Mortality
- Lamhokke
- Managing the pregnant ewe
- Mating on Lucerne lands
- Mineral and Vitamin supplementation effect on reproduction in Angora goats
- Oestrus and Mating in Angora Goats
- Out of Season Breeding in Angora goats
- Paraphimosis of the penis
- Performance Testing - Angora goat breeding
- Pigment in Angora goats
- Rams per Ewe Ratio
- REPEATABILITY and HERITIBILITY traits
- Selection for Body Weight in Angora Kids and Young Goats
- Semen Freezing And Subsequent Insemination In Angora Goats
- Synchronisation Program for Angora Goats
- Teaser Rams
- Testicle Traits
- The Weak and Cold (Hypothermic) Angora Kid
- Testicle Abnormalities in Angora Goats
- Vaginal Prolapse
- Weaning shock in Angora goat kids
- Weaning - The Angora goat ewe
- Weaning the Angora Goat Kid
- Vaccines
- Anthrax Vaccination in Angora Goats
- Clostridium and Pasteurella Vaccine (update)
- Orf, Scabby Mouth, ‘Vuilbek’ Vaccination
- Pasteurella Vaccines
- Rift Valley Fever Seroconversion
- Rift Valley Fever (RVF) - Vaccinating Maiden Ewes Each Year
- Vaccine Handling
- When to Vaccinate
- What vaccine cover do Angora goats need?
- Bio Security
- Procedures and Protocols
- Angora Goat First Aid
- Animal Identification - Tattooing
- Body Condition Score
- CAESARIAN by Veterinarian
- Castration - Burdizzo
- Euthanasia Protocols
- Faecal Egg Count - How to do
- Fire Burn Wounds in Angora Goats
- Handling Angora Goats
- Health Check on Angora Goats
- Hoof Care
- Horn Trimming
- How to conduct a basic Post Mortem on an Angora Goat
- How to dose an Angora goat
- How to perform a castration on Angora Goat
- Injecting Angora goats
- Lancing an-Abscess
- Mohair Disease Surveillance
- Paraphimosis of the penis
- Plunge Dipping
- Shearing Guidelines
- Shearing Wounds
- Stomach Tube
- Stress in Angora Goats
- Transporting Angora goats